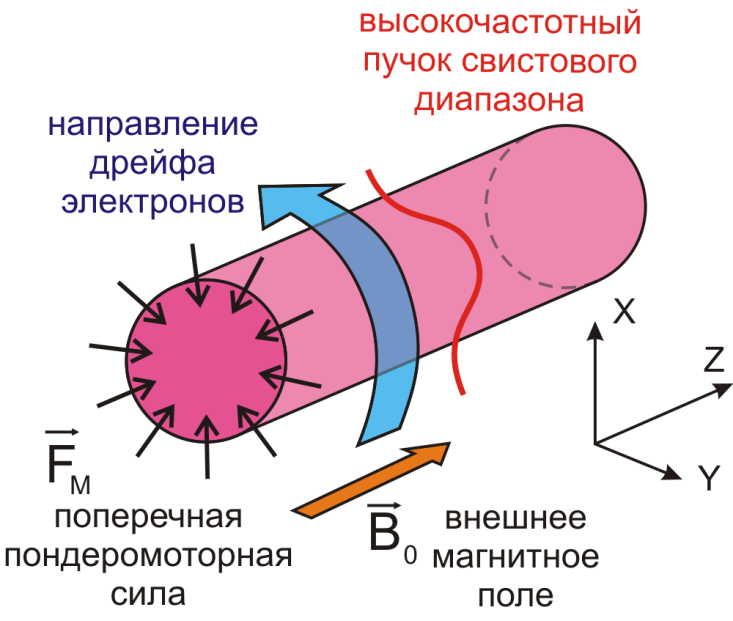
Генерация квазистационарного магнитного поля высокочастотной волной
В экспериментах на крупномасштабном плазменном стенде «Крот» обнаружен новый эффект – генерация квазистационарного магнитного поля (КМП) в слабостолкновительной замагниченной плазме в пространственно-неоднородном высокочастотном поле свистового диапазона частот. Источниками КМП являются нелинейные токи, возбуждаемые за счет продольной и поперечной компонент усредненной пондеромоторной силы, действующей на заряженные частицы в пространственно локализованном высокочастотном поле накачки.
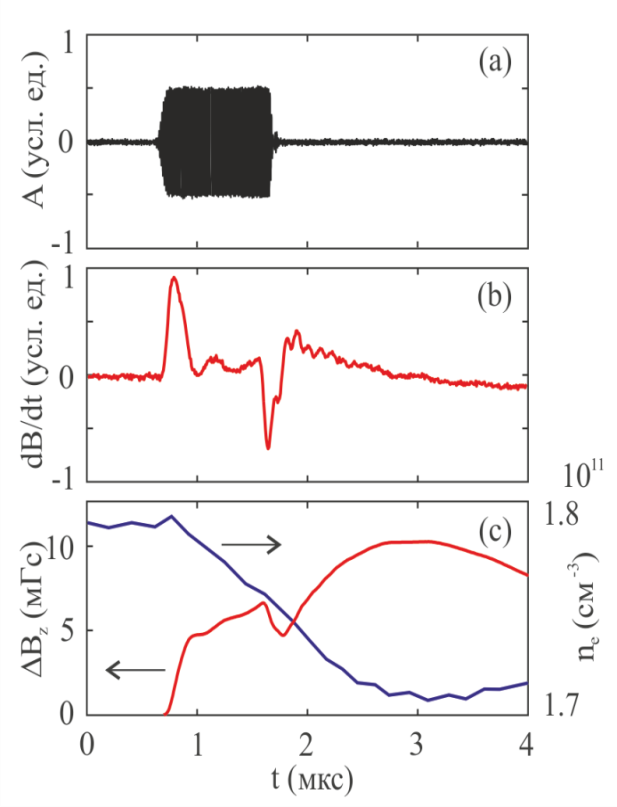
Исследована динамика возбуждаемых магнитных полей и квазистационарных токов, обнаружено, что время установления КМП определяется временем включения высокочастотного поля, а перенос импульсных токов и магнитных полей из области их генерации происходит со скоростью низкочастотных свистовых волн. Эффект может использоваться для генерации низкочастотных волн в активных ионосферных экспериментах. Исследование выполнено при поддержке Российского фонда фундаментальных исследований (проект № 10-02-01417-а).
Айдакина Н.А., Гущин М.Е., Зудин И.Ю., Коробков С.В., Костров А.В., Стриковский А.В. «Квазистационарное магнитное поле, возбуждаемое радиоимпульсом свистового диапазона частот» // Письма в ЖЭТФ, 2011, Т. 93, № 9, С. 555–560.